Food Chain Definition Ecology
The definition of a food chain is a system where a small animal is the food for a larger animal which in turn is the food for an even larger animal.
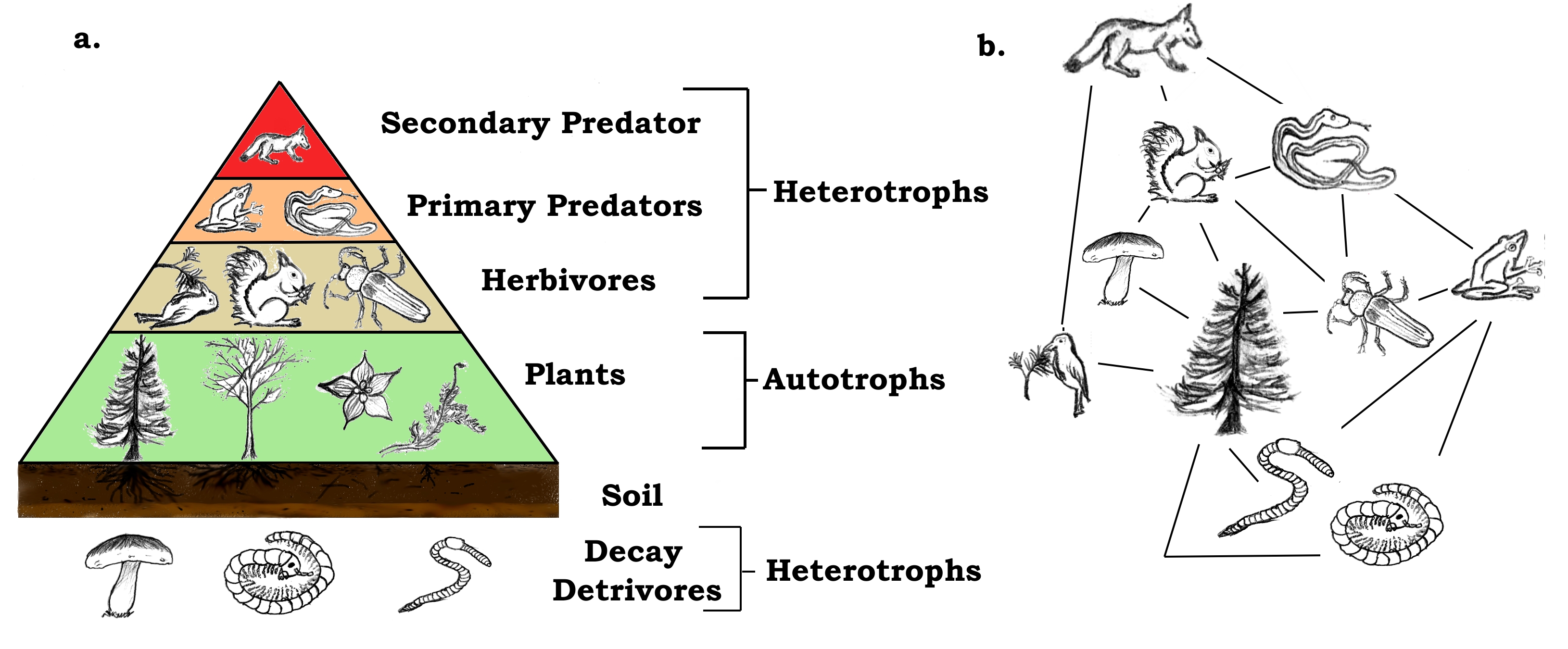
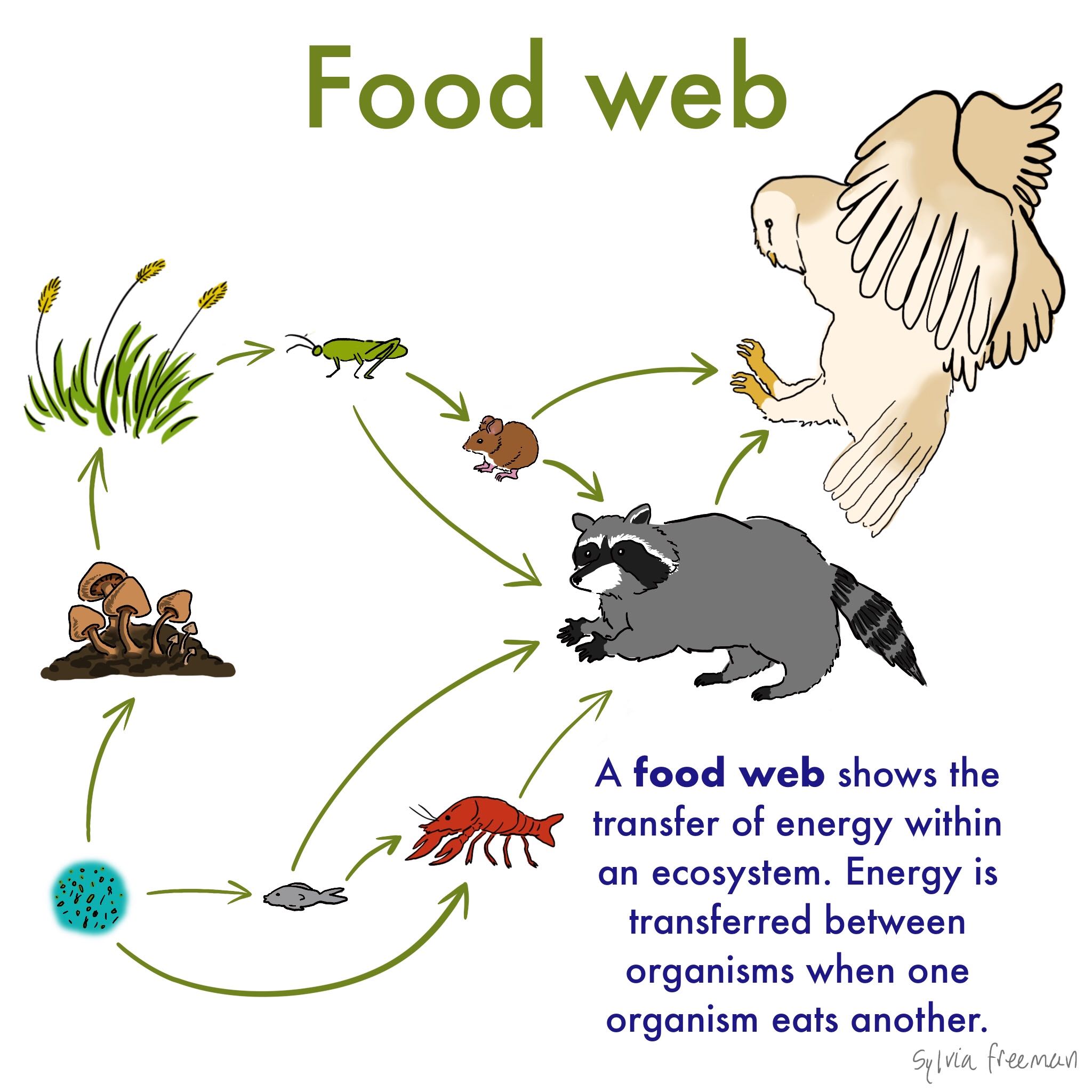
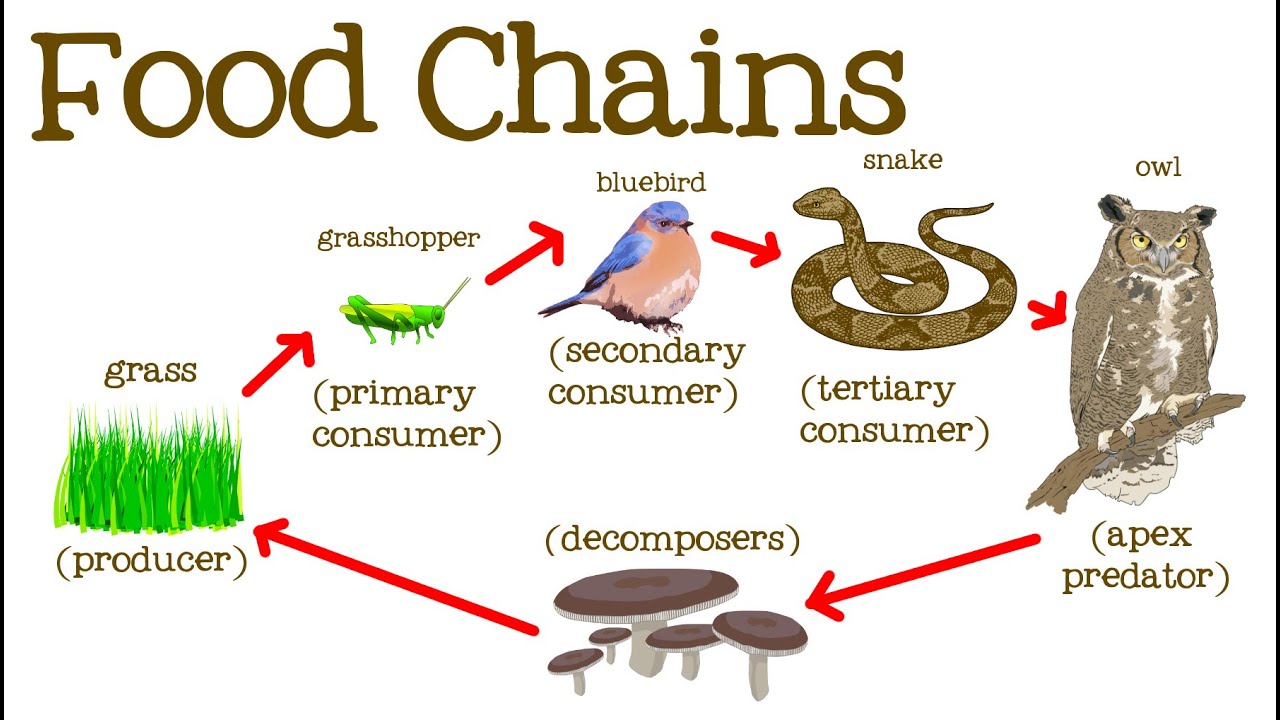
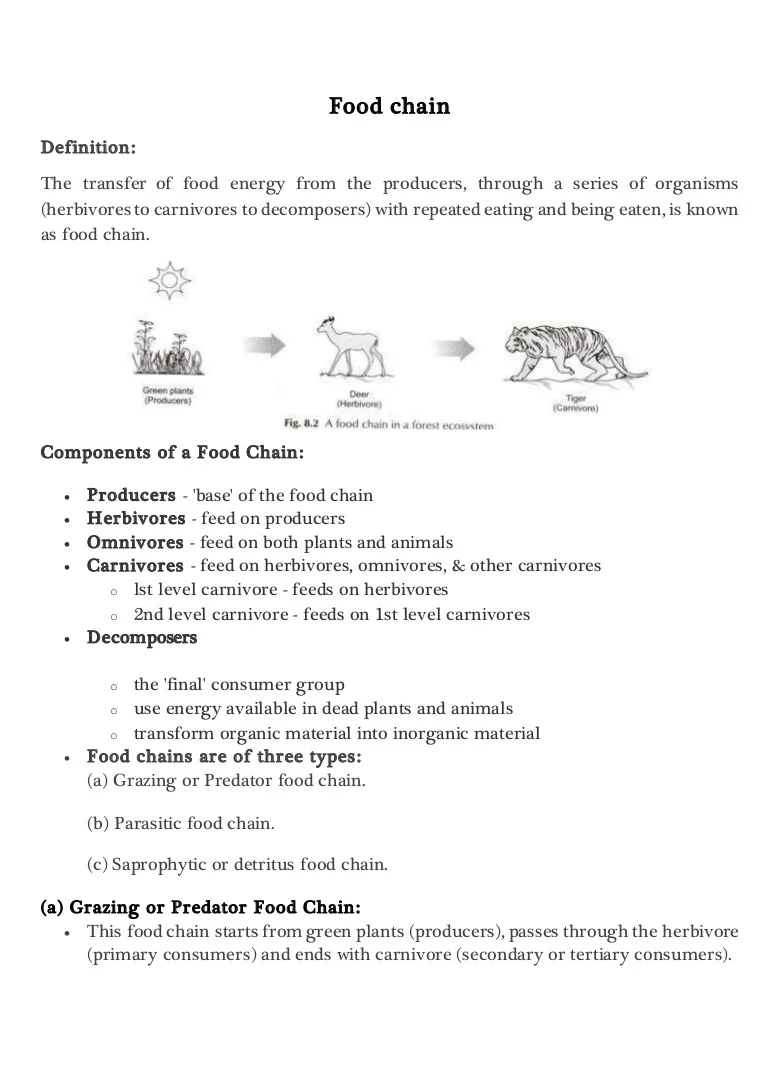
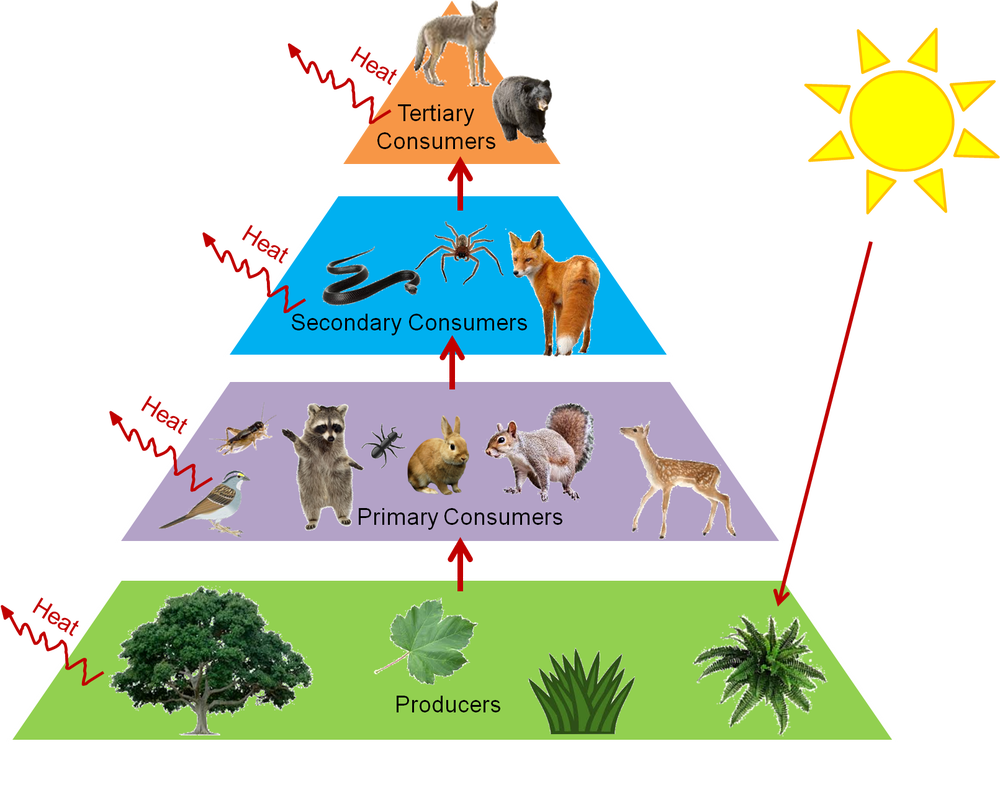
Food chain definition ecology. The food chain is a linear sequence of organisms where nutrients and energy is transferred from one organism to the other. This cyclic transfer of food and the relation of food and its consumer are known as the food chain. Depending on producer and different levels of consumers some examples of food chain are given below.
The sun is the initial source of energy which provides energy for everything on the planet. In ecology a food chain is a series of organisms that eat one another so that energy and nutrients flow from one to the next. The food chain is an ideal representation of flow of energy in the ecosystem.
This occurs when one organism consumes another organism. The sequence of the transfer of food energy from one organism to another in an ecological community. The food chain describes who eats whom in the wild.
A food chain in a grassland ecosystem may consist of grasses and other plants grasshoppers frogs snakes and hawks figure 83. Food ecology is the science which looks at the food production process and assesses the impact each stage of the process has on how plants and animals relate. Video about Food Chain Definition Ecology.
In scientific terms a food chain is a chronological pathway or an order that shows the flow of energy from one organism to the other. Forest ecosystem food chain Google Search Forest meaning pronunciation translations and examples. It begins with producer organism follows the chain and ends with decomposer organism.
The sequence of organism through which the energy flows is known as food chain. These easy recipes are all you need for making a delicious meal. The food chain is a linear sequence of organisms where nutrients and energy are transferred from one organism to another.