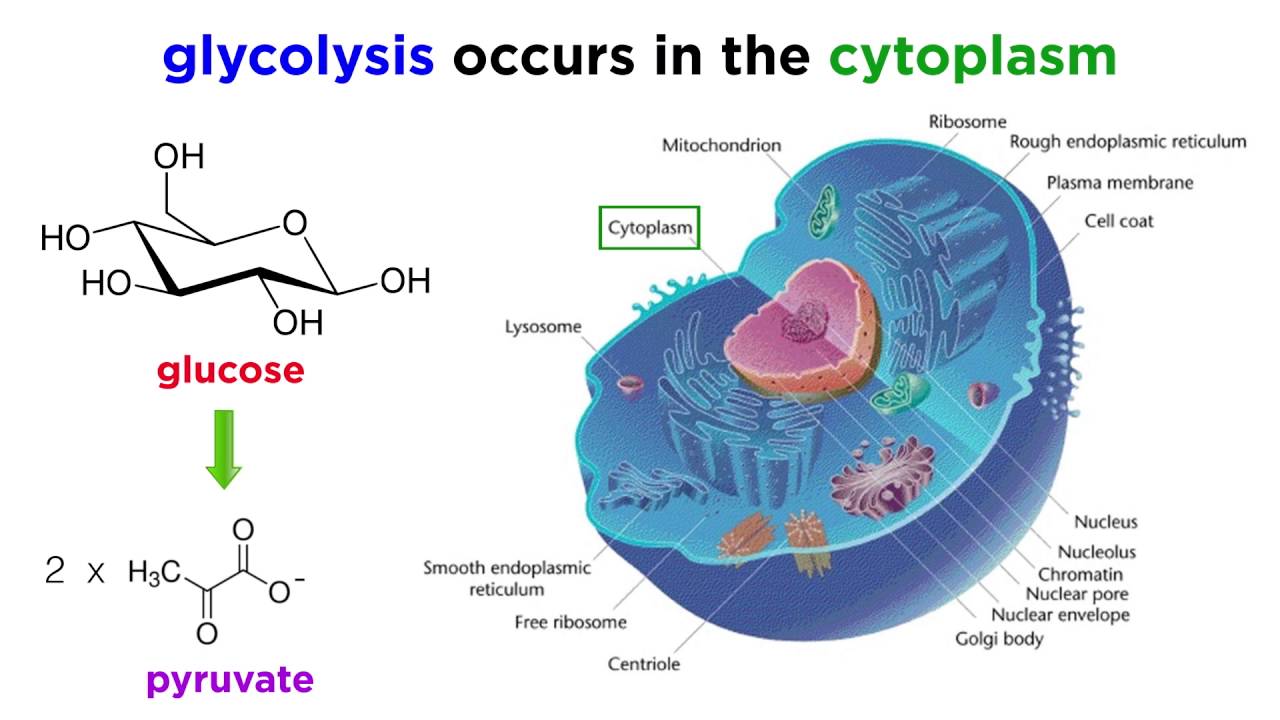
Cellular Respiration Meaning In Biology

ATP for use in energy-requiring activities of the cell.
Cellular respiration meaning in biology. Cellular respiration refers to both aerobic and anaerobic respiration but is often synonymous with aerobic respiration. The process plays an essential role in maintaining the biological functions of all living cells. Anaerobic respiration is another type of cellular respiration that takes place in the absence of oxygen and produces energy.
Both aerobic and anaerobic respiration involve chemical reactions which take place in the cell to produce energy which is needed for active processes. Where cellular respiration happens. But cellular respiration is slightly more complicated than just converting the energy from glucose into ATP.
Glycolysis consists of an energy-requiring phase followed by an energy-releasing phase. Organisms that do not depend on oxygen degrade foodstuffs in a process called fermentation. Introduction to Cellular Respiration.
Glucose and then stored in energy-carrying biomolecule eg. In contrast to simple combustion cellular respiration involves the step-wise release of energy in a tightly regulated fashion. Cellular respiration can be described as the reverse or opposite of photosynthesis.
Google Classroom Facebook Twitter. In this process glucose breaks down without the help of oxygen and the by-products produced are alcohol CO2 and energy or ATP. To create ATP and other forms of energy to power cellular reactions cells require fuel and an electron acceptor which drives the chemical process of turning energy into a useable form.
Aerobic respiration requires oxygen to fully oxidise the organic molecule. Cellular respiration is a set of metabolic reactions and processes that take place in the cells of organisms to convert chemical energy from oxygen molecules or nutrients into adenosine triphosphate ATP and then release waste products. Cellular respiration Energy from nutrients is converted into ATP.