Cellular Respiration Equation Definition
Cellular Respiration Definition A series of metabolic reactions that takes place within the cell is called cellular respiration.
Cellular respiration equation definition. Its overall chemical reaction of cellular respiration equation is simplified as. The chemical formula for the overall process is. This process can be explained with the help of the chemical equation.
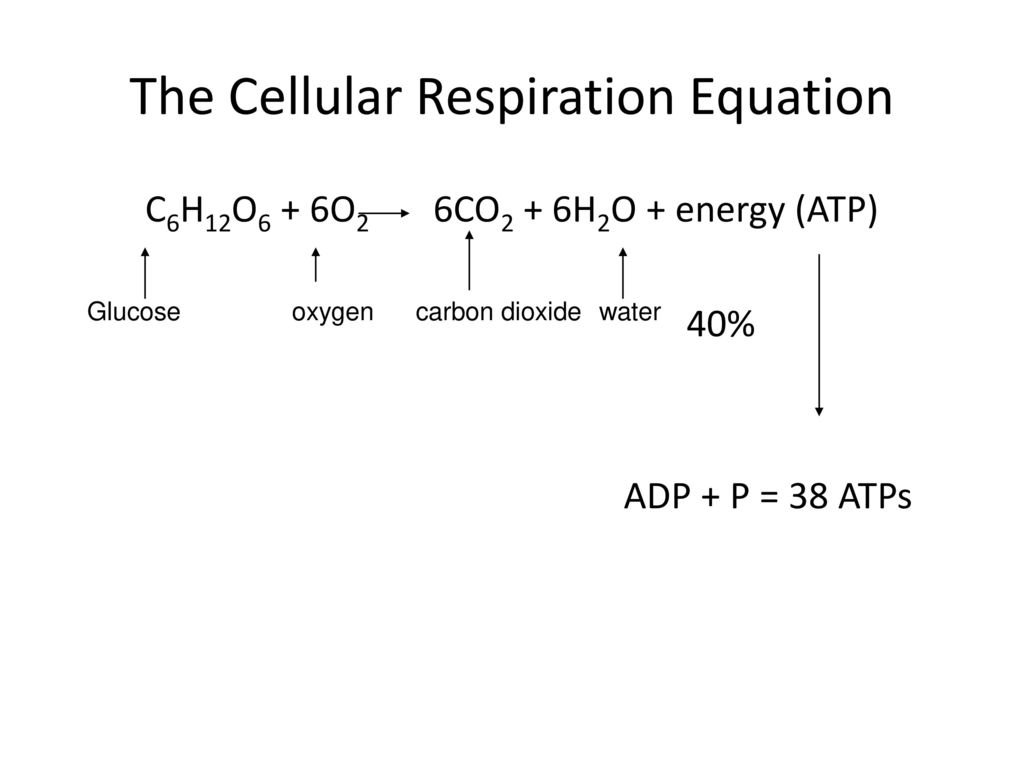
C 6 H 12 O 6 6 O 2 6 CO 2 6 H 2 O 38ATP Glucose 6. Cellular respiration takes place in the living cells of organisms. What is Cellular Respiration Definition Facts types 2.
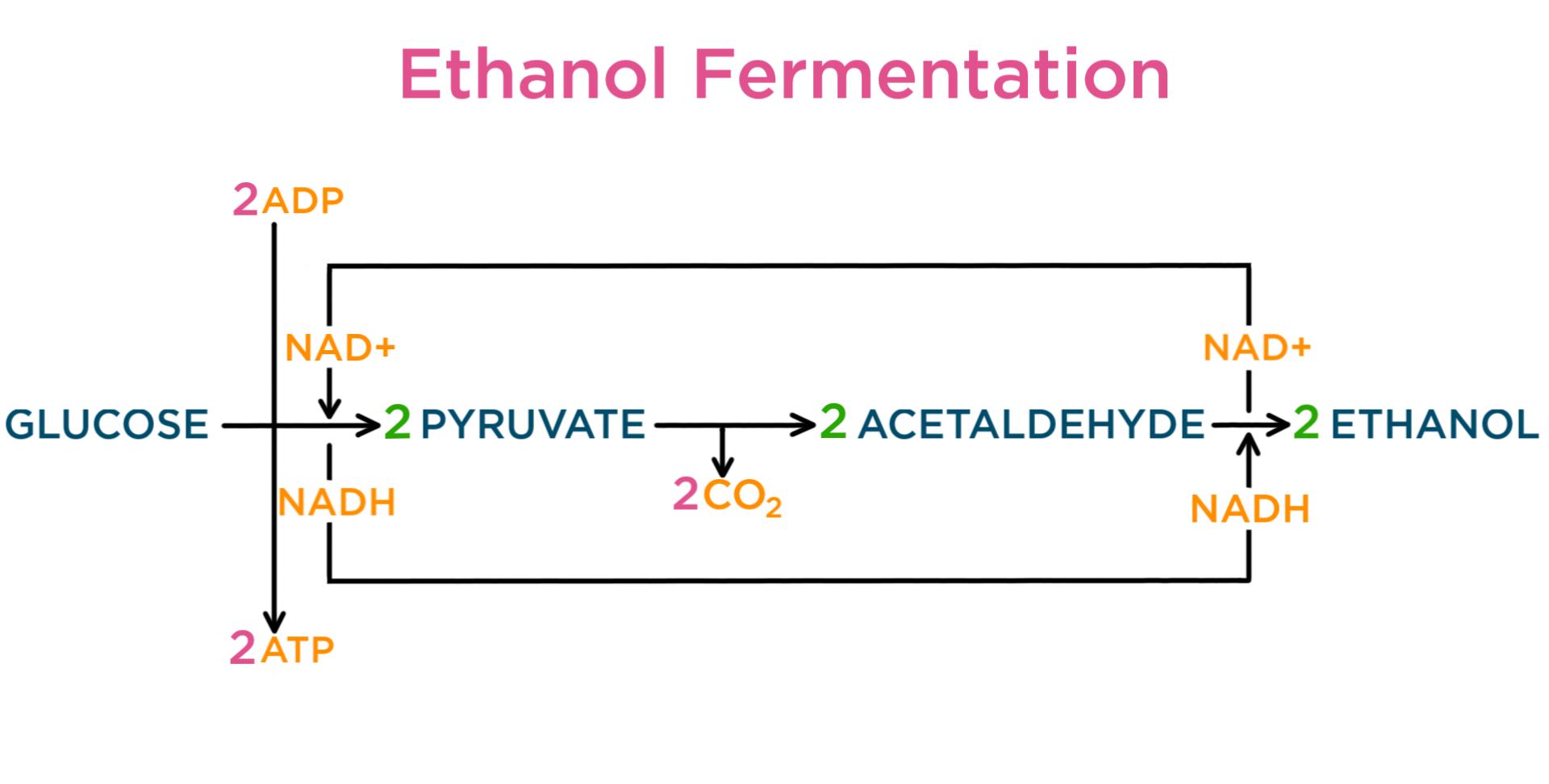
Aerobic or respiration in the presence of oxygen and anaerobic or respiration without oxygen. This series of biochemical reactions is also called a metabolic pathway Two types of cellular respiration exist. The word equation for cellular respiration is.
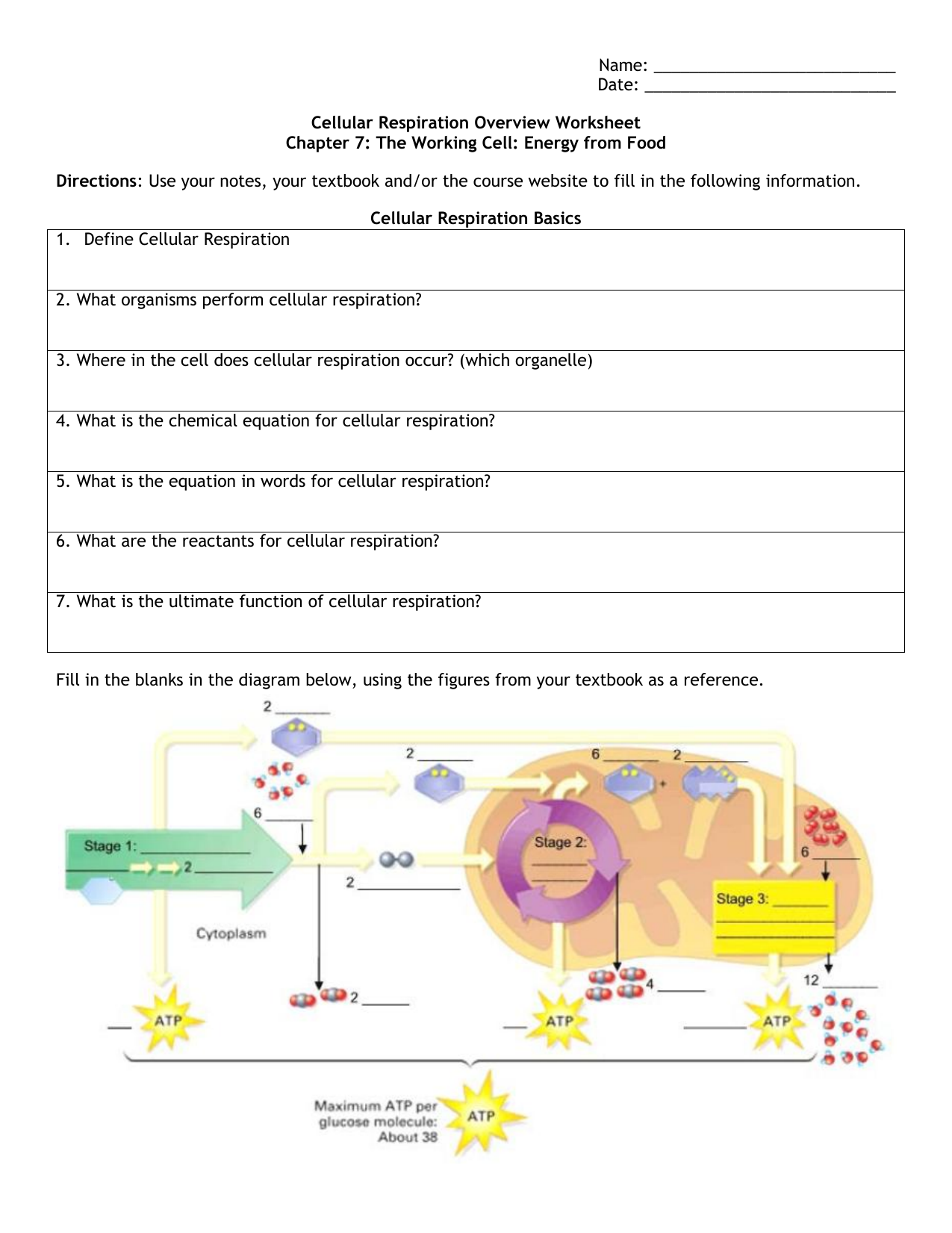
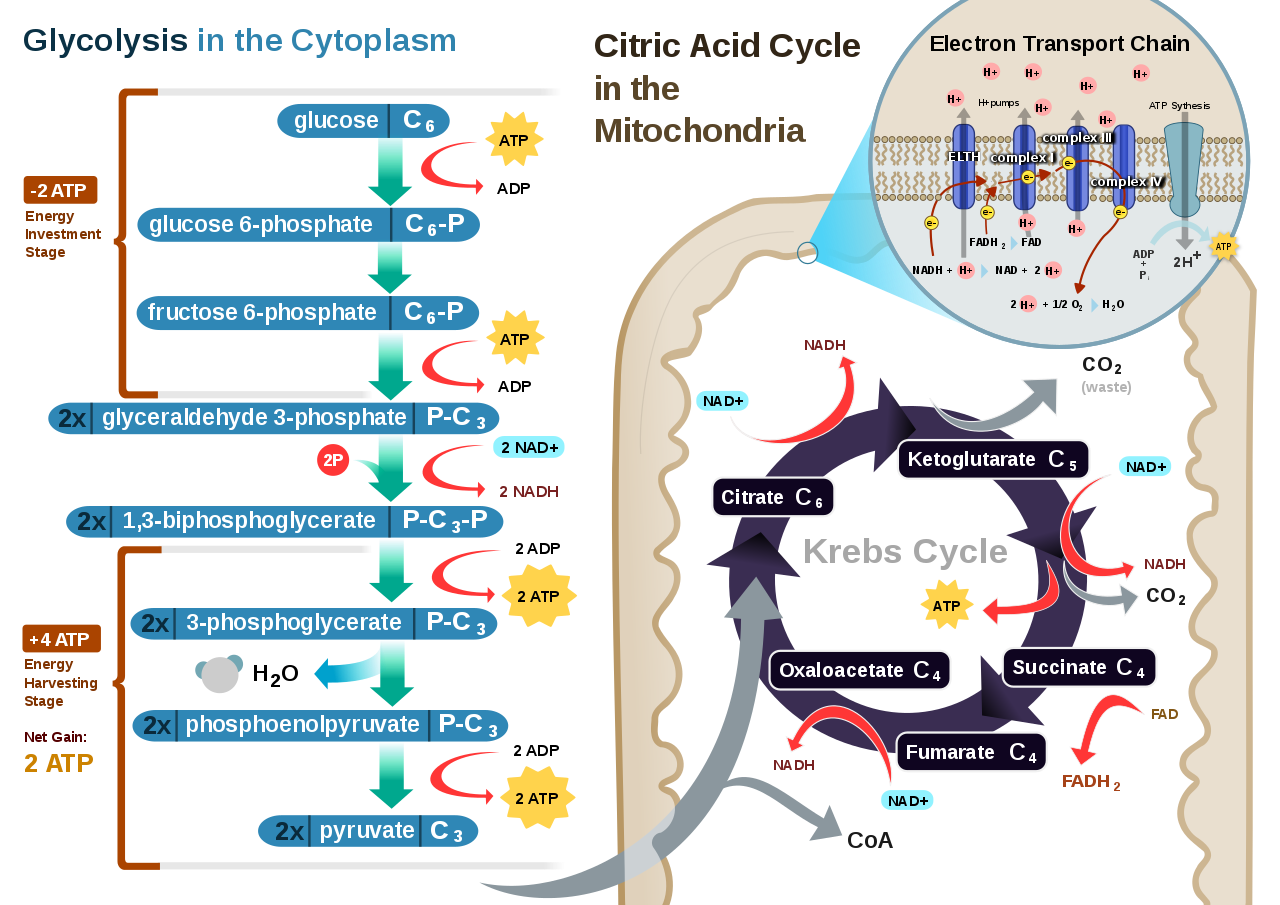
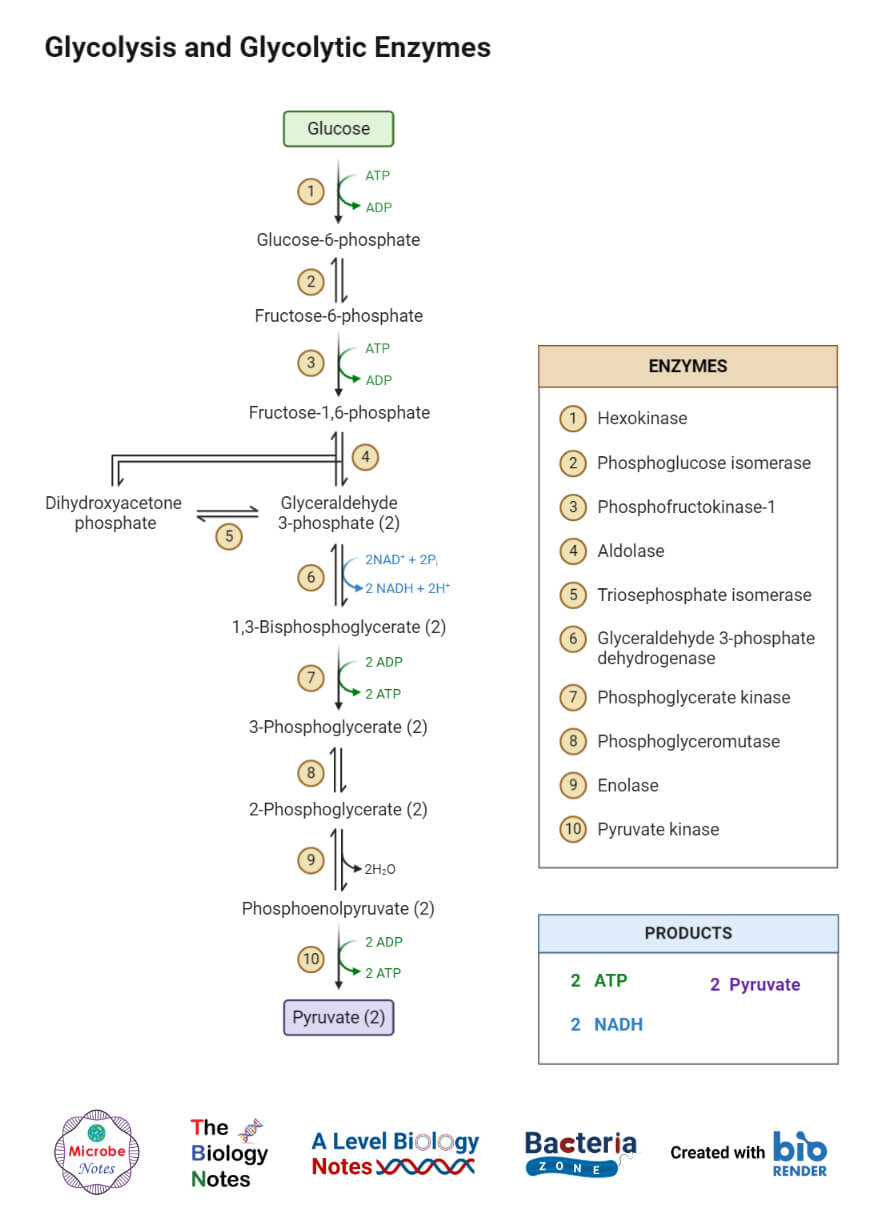
In this process water and carbon dioxide are produced as end products. Cellular respiration is a set of metabolic reactions and processes that take place in the cells of organisms to convert chemical energy from oxygen molecules or nutrients into adenosine triphosphate and then release waste products. The process takes place in four stages.
C 6 h 12 o 6 6 o 2 6 co 2 6 h 2 o energy as atp the word equation for this is. Cellular respiration is the process through which cells convert sugars into energy. There are three main stages of cellular respiration.
GlucoseC 6 H 12 O 6 Oxygen6O 2 Carbon dioxide6CO 2 Water6H 2 O Energy ATP. C 6 H 12 O 6 1 glucose molecule 6 O 2 6 CO 2 6 H 2 O 36 ATP ENERGY carbohydrate oxygen carbon dioxide water ATP energy 2 Description of the molecules created in all three stages of cellular respiration. The process involves harvesting biochemical energy from organic molecules especially glucose is converted into ATP adenosine triphosphate.







:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/cellular_respiration_3-58b9a5415f9b58af5c839e04.jpg)